Carbon Filtration
Water Purification to Remove CTO and VOC
What is the Purpose of a Carbon Filter?
Removal of CTO
Remove Chlorine, Bad Taste, Odor in Water
Removal of VOC
Remove Volatile Organic Compounds such as pesticides
Improves Taste & Smell
Improves the taste and smell of water
Charcoal, the burnt product of bamboo or husk, is predominantly made of pure carbon. When used as a filter, this Carbon or Charcoal filter acts as a natural medium to remove Chlorine, Taste, Odor (CTO) and Volatile Organic Compounds (VOC) like pesticides. It has also proved to be able to improve the taste and smell of water – especially beneficial in Singapore given chlorine is often added to water supplied by the Public Utilities Board (PUB).
What is Granular Activated Carbon (GAC) Filtration?
The heating of organic matter, such as coal, wood and coconut shell, in the absence of air, which is then being crushed into granules, produces Granular Activated Carbon (GAC). This material is a highly porous adsorbent. This end product can be said to have remarkable taste, odor, and chlorine reduction capabilities. Such capabilities are extremely important given chlorine and chloramines used by water treatment plants to treat water can create carcinogenic by-products that lingers in drinking water - tainting it with an artificial, chemical flavor.
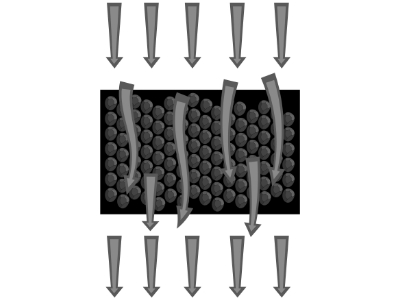
Such a capability is achieved in the following process. When the water flows in one direction through the cartridge and contacts the carbon filter, the positively charged GAC attracts negative ions such as ozone, chlorine, fluorides and dissolved organic solutes from the water. The loose granules of activated carbon then allow water to flow through easily while the contaminants adheres to the surface of the carbon filter.
Despite such capabilities there are three main problems associated with GAC filters. They are channeling, dumping, and an inherently large pore size. However, these problems are not attributed to the activated carbon filtration media, instead, are attributed to the design of the filters and the use of loose granules of activated carbon.
What is Carbon Filter?

The World Health Organization (WHO) has recommended the use of carbon filters for the removal of Chlorine, Taste, Odor (CTO) and Volatile Organic Compounds (VOC) like pesticides in waters.
These carbon filters can be manufactured from either coal, wood, nut shells or bamboo. Its roots can be traced all the way back to Egyptian times where the use of carbon as a filter to purify water was popular. It was discovered then that carbon is a powerful absorbent that has the ability to absorb contaminants during water filtration.
However, in recent years, coconut shell carbon has become the preferred material to manufacture carbon filters in the industry. The reason is simple, coconut shell is a renewable resource and 85-90% surface area of coconut shell are micro-pores. These micro-pores allow a greater number of contaminants to be effectively trapped. These impurities are trapped inside the micro-pore structure of the carbon substrate. For ease of understanding, the micro-pores in the carbon filter act as parking spaces for contaminants to be trapped while water flows through.
What is Activated Carbon filter?
Activated Carbon used in filters are carbon that undergo ADDITIONAL processing that further opens the pores of the carbon filter. This increases the surface area, giving the carbon filter MORE CAPACITY to trap contaminants.
Types of Activated Carbon Filters
Activated carbon filters are generally categorized by micron size, method of preparation, and industrial application. The 3 most common types of activated carbon filter used in water filtration are as follows:
Granular Activated Carbon (GAC) filter is made up of individual carbon granules providing an easy channel for filtration as compared to other types of activated carbon filters. GAC is usually selected because it is most economical and can maintain a good water flowrate and pressure, without compromising filtration.
Powdered Activated Carbon (PAC) has fine particles made from grounded or crushed activated carbon. They are particles used in activated carbon block filters. Given activated carbon block consists of much finer carbon granule than GAC, the surface area of PAC is larger than GAC. This makes the carbon block much more effective than GAC. Unfortunately, this compromises the flowrate of water, results in lower pressure and require higher frequency of filter change.
Impregnated Carbon are carbon particles containing inorganic impregnated compounds such as silver. Silver loaded activated carbon that can inhibit the growth of microbes are often used as adsorbent in water purification processes. Due to its antimicrobial and antiseptic properties, silver-impregnated carbon works an effective adsorbent for purification in earth-bound, domestic water systems. However, this is not commonly used in Singapore because Singapore water is already disinfectant with chlorine.
How Often should I Change the Activated Carbon filter?
Blue Heale recommends a maximum 12 months usage for a single 10” GAC Activated Carbon filter. The reason is as follows. Since Activated Carbon Filters are introduced to remove chlorine from water, once the Activated Carbon Filter are “fully parked” and can no longer trap anymore chlorine and contaminants, it will have to be changed.